Admin Configuration
After installing the Query Runner application, administrators must configure SQL Studio for each database service. This configuration determines which authentication methods are available to users and what connection settings they can override.
Configuration Overview
Prerequisites
Before configuring SQL Studio for any database service:
- Ensure the database service is already configured in Collate
- Service connection should be working (metadata ingestion successful)
- For Collate SSO: Google OIDC SSO must be configured in Collate (Settings → Security → SSO)
- For OAuth: You must have OAuth credentials (Client ID and Client Secret) from your OAuth provider
Accessing Service Configuration
- Navigate to Settings → Services → Database Services
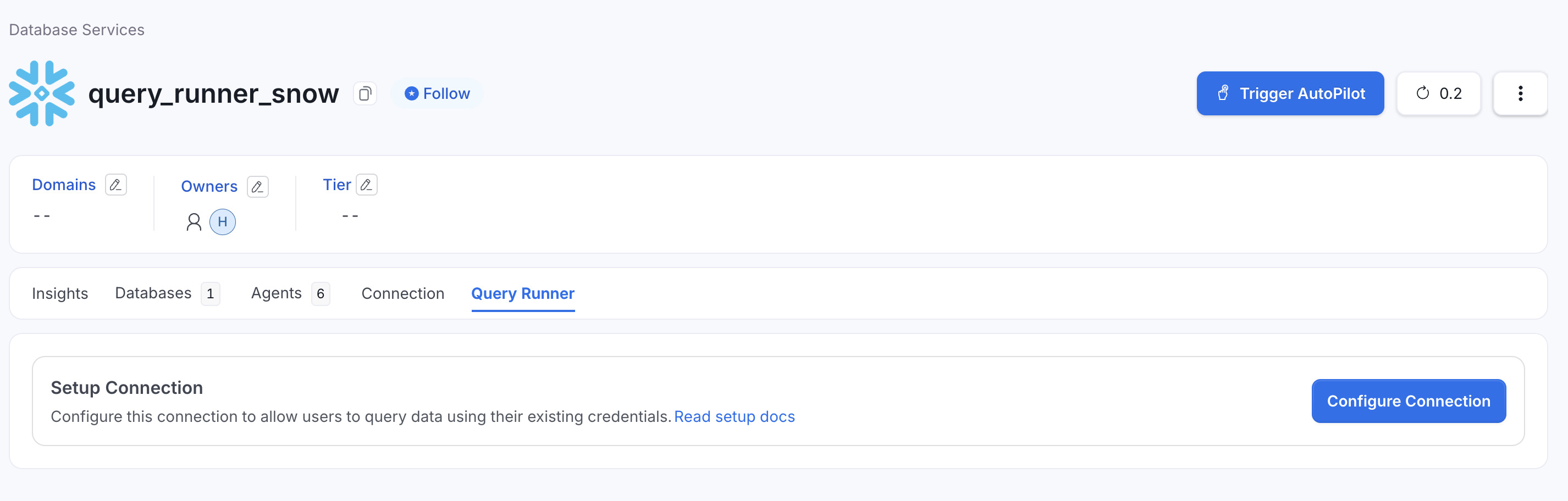
Navigate to Settings → Services → Database Services
- Select the database service you want to configure (e.g.,
my-bigquery,production-snowflake) - Click on the Query Runner tab
- Click Configure Connection to begin setup
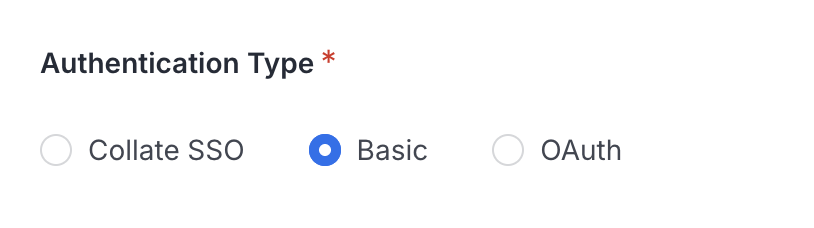
Select authentication type for SQL Studio
SQL Studio must be configured separately for each database service. You can configure multiple services with different authentication methods based on your security requirements.
Common Configuration Settings
All services share these configuration options:
| Setting | Description | Default | Allowed Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authentication Type | How users authenticate to the service | Varies | CollateSSO, OAuth, Basic |
| Enabled | Whether SQL Studio is active for this service | false | true / false |
Important: SQL Studio is disabled by default. You must toggle Enabled to ON to make it available to users after configuration.
BigQuery Configuration
BigQuery supports three authentication methods: Collate SSO, OAuth, and Basic Authentication.
Authentication Method 1: Collate SSO
Recommended for: Organizations using Google OIDC for Collate login
Collate SSO leverages your existing Google SSO configuration in Collate to authenticate with database services. Instead of configuring separate OAuth credentials, SQL Studio automatically uses already configured fields from Collate login.
SSO Support: As of now, Collate SSO flow is only supported for Google OIDC (OpenID Connect).
Configuration Steps:
In the Query Runner configuration form, select Authentication Type → Collate SSO
OAuth Credentials (auto-populated):
- Client ID: (automatically fetched from Google OIDC SSO configuration)
- Client Secret: (automatically fetched from Google OIDC SSO configuration)
- Scope: (automatically set to include BigQuery scope:
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bigquery) - Redirect URL: (auto-generated based on your Collate domain)
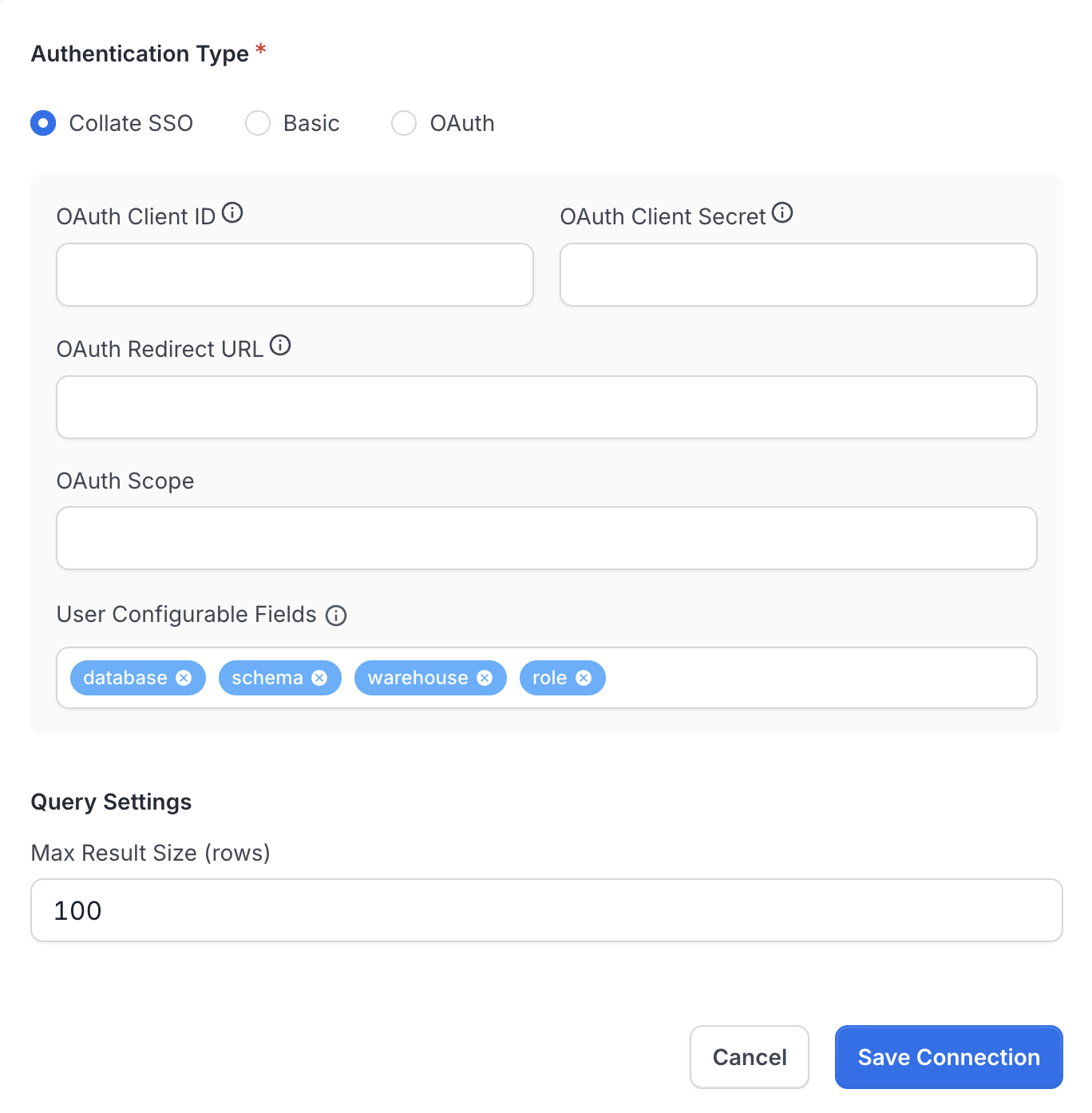
Collate SSO authentication configuration with auto-populated fields
Click Save Configuration
OAuth credentials are automatically prefetched from your Collate's Google SSO settings
After saving, you can view the auto-enriched values in the configuration
Toggle Enabled to ON to activate SQL Studio for this service
Click Save again to apply changes

Query Runner tab after successful configuration
Prerequisites:
- Google OIDC SSO must be configured in Collate (Settings → Security → SSO)
- SSO OAuth app must have BigQuery API scope enabled
- Users must have BigQuery permissions in their Google Cloud projects
Authentication Method 2: OAuth
Recommended for: Organizations that want OAuth but use a different SSO provider or email & password for Collate login (e.g., Okta, Auth0, Email/Password)
OAuth allows users to authenticate directly with Google OAuth 2.0, separate from their Collate login.
Configuration Steps:
Step 1: Create Google OAuth App (if not already created)
- Go to Google Cloud Console
- Navigate to APIs & Services → Credentials
- Click Create Credentials → OAuth 2.0 Client ID
- Application type: Web application
- Name:
Collate SQL Studio - BigQuery - Authorized redirect URIs: Add
https://your-collate-domain.com/api/v1/queryRunner/oauth/callback- Replace
your-collate-domain.comwith your actual Collate domain - Ensure the URL is exactly
https://(nothttp://) for production
- Replace
- Click Create
- Copy the Client ID and Client Secret (you'll need these in Step 2)
Keep credentials secure: Store your Client ID and Client Secret in a secure location (e.g., 1Password, AWS Secrets Manager). Never commit them to version control.
Step 2: Configure in Collate
In the Query Runner configuration form, select Authentication Type → OAuth
Enter OAuth Client Credentials:
- Client ID: Paste from Google Cloud Console
- Client Secret: Paste from Google Cloud Console
- Redirect URL:
https://your-collate-domain.com/api/v1/queryRunner/oauth/callback(verify exact match) - Scope:
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bigquery(default)
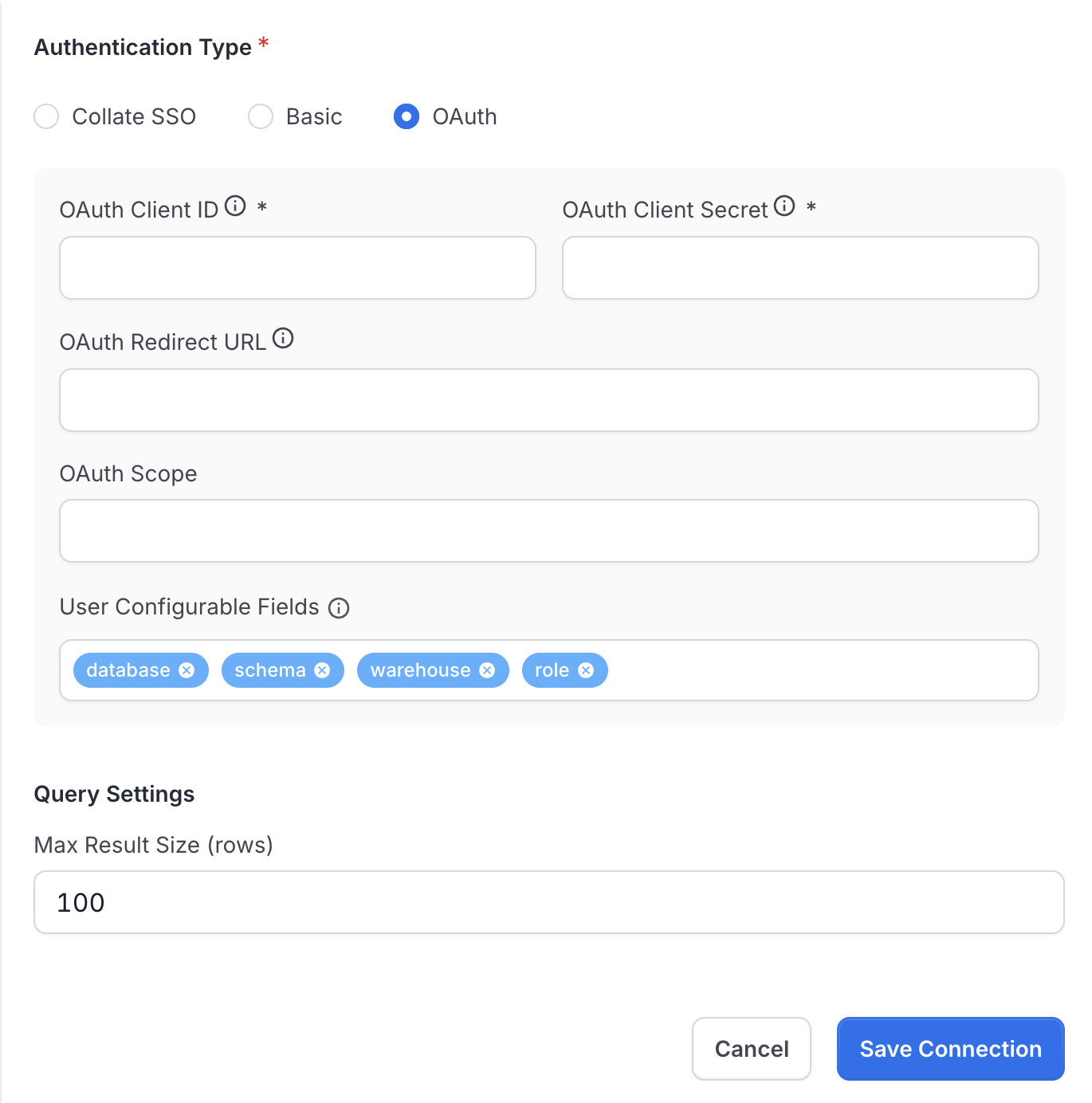
Configure OAuth authentication with client credentials
Toggle Enabled to ON to activate
Click Save Configuration
Authentication Method 3: Basic Authentication (Service Account)
Recommended for: Service accounts, automated access, or when OAuth is not feasible
Basic Authentication allows users to provide their own GCP Service Account credentials.
Setup Steps:
- In the Query Runner configuration form, select Authentication Type → Basic
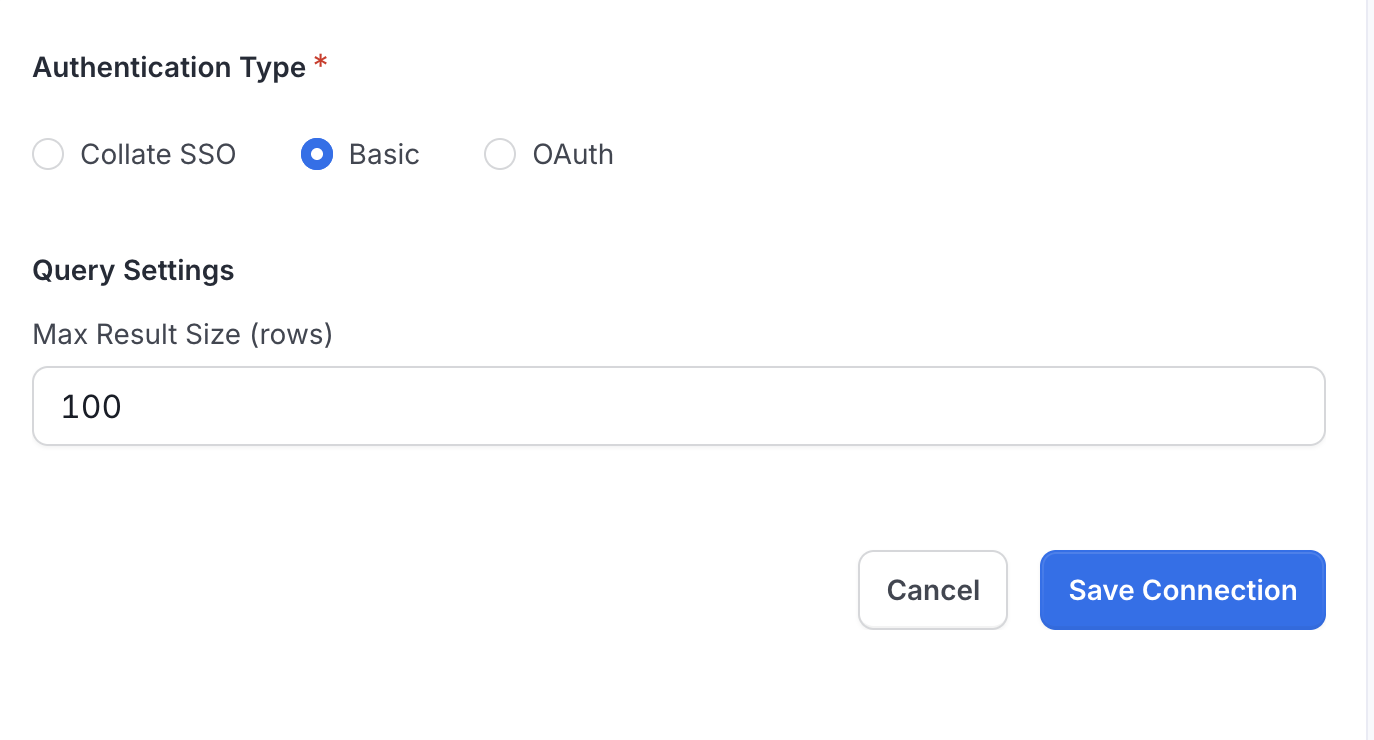
Configure Basic Authentication for SQL Studio
Toggle Enabled to ON to activate
Click Save Configuration
User Requirements:
- Each user must have a GCP Service Account with BigQuery permissions
- Service Account must have
bigquery.jobs.createpermission - Users will upload their Service Account JSON file or enter credentials manually
Snowflake Configuration
Snowflake supports OAuth and Basic Authentication.
Authentication Method 1: OAuth
Recommended for: Organizations with Snowflake OAuth integration configured
Prerequisites:
- Snowflake OAuth Security Integration must be created (see setup below)
Setup Steps:
- Create Snowflake OAuth Security Integration (run in Snowflake):
- Retrieve OAuth Credentials (run in Snowflake):
This returns JSON with OAUTH_CLIENT_ID and OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET.
- Configure in Collate:
- In the Query Runner configuration form, select Authentication Type → OAuth
- Enter OAuth Client Credentials:
- Client ID: From step 2
- Client Secret: From step 2
- Redirect URL:
https://your-collate-domain.com/api/v1/queryRunner/oauth/callback - Scope:
session:role-any(or specific role scope likesession:role:ANALYST)
- (Optional) Enable User Configurable Fields:
- ☑️ Warehouse: Allow users to select compute warehouse
- ☑️ Database: Allow users to select default database
- ☑️ Schema: Allow users to select default schema
- ☑️ Role: Allow users to select their Snowflake role
- Toggle Enabled to ON to activate
- Click Save Configuration
Authentication Method 2: Basic Authentication
Recommended for: Username/password or key-pair authentication
Setup Steps:
- In the Query Runner configuration form, select Authentication Type → Basic
- (Optional) Enable User Configurable Fields:
- ☑️ Warehouse: Allow users to override warehouse
- ☑️ Database: Allow users to override database
- ☑️ Schema: Allow users to override schema
- ☑️ Role: Allow users to override role
- Toggle Enabled to ON to activate
- Click Save Configuration
User Requirements:
- Users must have Snowflake credentials (username/password or key-pair)
- For key-pair auth, users must upload their public key to Snowflake
Trino Configuration
Trino (Starburst) currently supports OAuth only.
Authentication Method: OAuth
Recommended for: Starburst Galaxy or Trino clusters with OAuth configured (typically Azure AD)
Prerequisites:
- Trino/Starburst cluster must have OAuth authentication enabled
- OAuth provider (e.g., Azure AD, Okta) must be configured
Setup Steps:
Create OAuth App in Azure AD (example for Starburst):
- Go to Azure Portal → Azure Active Directory → App registrations
- Click New registration
- Name:
Collate SQL Studio - Trino - Redirect URI:
https://your-collate-domain.com/api/v1/queryRunner/oauth/callback - Click Register
- Go to Certificates & secrets → New client secret
- Copy the Application (client) ID and Client secret value
Configure in Collate:
- In the Query Runner configuration form, select Authentication Type → OAuth
- Host Port: Auto-populated from database service connection (e.g.,
ometa.galaxy.starburst.io:443) - Enter OAuth Client Credentials:
- Client ID: From Azure AD
- Client Secret: From Azure AD
- Redirect URL:
https://your-collate-domain.com/api/v1/queryRunner/oauth/callback - Scope:
openid profile email(or custom scope)
- Toggle Enabled to ON to activate
- Click Save Configuration
Configuration Best Practices
Choosing Authentication Methods
| Scenario | Recommended Method |
|---|---|
| Collate uses Google SSO + BigQuery | Collate SSO |
| Collate uses non-Google SSO + BigQuery | OAuth |
| Automated/service account access | Basic Authentication |
| Snowflake with OAuth integration | OAuth |
| Snowflake without OAuth | Basic Authentication |
| Trino/Starburst | OAuth (only option) |
User Configurable Fields
Enable user-configurable fields to give users flexibility while maintaining security:
| Field | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset (BigQuery) | Users work in different datasets | analytics, marketing, sales |
| Warehouse (Snowflake) | Users have different compute needs | COMPUTE_WH, LARGE_WH |
| Database (Snowflake) | Users access different databases | PROD, DEV, STAGING |
| Schema (Snowflake) | Users work in different schemas | PUBLIC, ANALYTICS |
| Role (Snowflake) | Users have different access levels | ANALYST, ENGINEER, ADMIN |
Allowing users to configure Role gives them flexibility but ensure Snowflake role permissions are properly configured to prevent unauthorized access.
Security Recommendations
- Use OAuth when possible: OAuth provides better security with token-based authentication
- Rotate OAuth credentials: Regularly rotate Client Secrets for OAuth apps
- Limit Max Result Size: Set to 100 or lower to prevent excessive data retrieval
- Audit configuration changes: Monitor who changes Query Runner configurations
- Test connections: Always test connections after configuration changes
Max Result Size Guidelines
| Use Case | Recommended Max Result Size |
|---|---|
| General querying | 100 rows (default) |
| Data exploration | 50 rows |
| Production analysis | 100 rows |
| Large datasets | 25 - 50 rows |
Users should use LIMIT clauses in their queries to control result size further.
Updating Configuration
To update an existing Query Runner configuration:
- Navigate to the service's Query Runner tab
- Click Edit Configuration
- Modify settings as needed
- Click Save
Changing Authentication Type: If you change the authentication type (e.g., from OAuth to Basic), all existing user connections will be deleted. Users will need to re-authenticate using the new method.
Enabling/Disabling SQL Studio
Enabling SQL Studio
After configuring authentication, you must enable SQL Studio for users:
- In the Query Runner configuration, toggle Enabled to ON
- Click Save Configuration
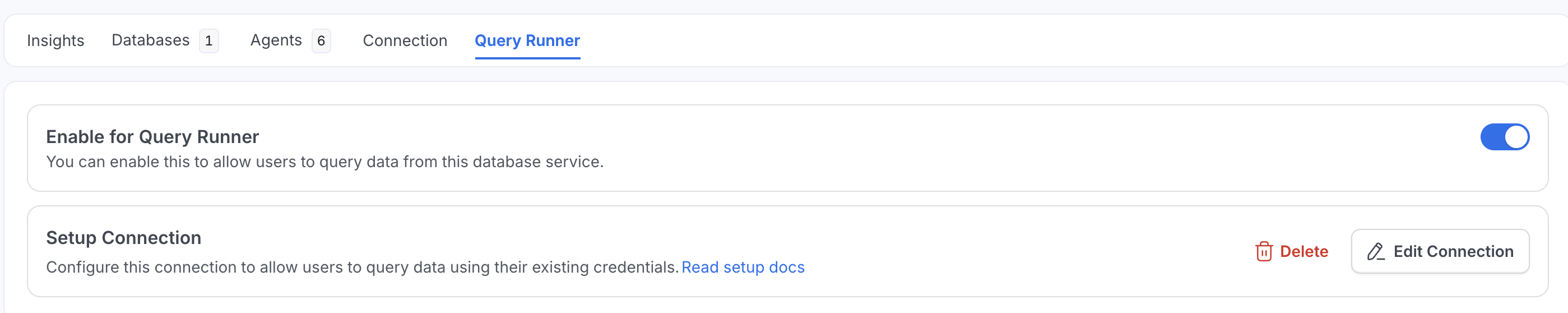
Check Enabled to activate SQL Studio for this service
Once enabled, the service will appear in SQL Studio for all users with appropriate permissions.
Disabling SQL Studio
To temporarily disable SQL Studio for a service:
- Navigate to the service's Query Runner tab
- Toggle Enabled to OFF
- Click Save
This prevents new user connections without deleting existing configurations. Users will see "Service not available" in SQL Studio.
Connection Status Indicators
Understanding connection status helps you troubleshoot user issues:
| Status | Color | Meaning | User Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connected | 🟢 Green | Active connection, ready to execute queries | None - user can run queries |
| Pending | 🟡 Yellow | Connection test in progress after authentication | Wait a few seconds |
| Not Connected | ⚪ Gray | No connection established | Click to authenticate |
Connection Flow
Connection Testing:
- After initial authentication, SQL Studio runs a test query (
SELECT 1) - This verifies credentials, permissions, and network connectivity
- If successful, status changes to Connected (green)
- If failed, error message displayed with details
Managing User Access
Who Can Use SQL Studio?
Users can access SQL Studio if they have:
- View Basic permission on the database service in Collate
- SQL Studio is enabled by administrator for that service
- They have successfully authenticated their connection
Controlling Access
Use Collate's role-based access control (RBAC):
- Assign users to teams with appropriate policies
- Grant View Basic permission on database services
- Users without permission won't see the service in SQL Studio
Deleting Configuration
To completely remove Query Runner configuration:
- Navigate to the service's Query Runner tab
- Click Delete Configuration
- Warning: This will permanently delete:
- Admin configuration
- All user connections for this service
- All saved queries for this service
- Type the service name to confirm
- Click Confirm Delete
Troubleshooting Configuration
OAuth Callback URL Mismatch
Problem: "Redirect URI mismatch" error during OAuth setup
Solution:
- Verify the redirect URL in Collate matches exactly:
https://your-collate-domain.com/api/v1/queryRunner/oauth/callback - Check for trailing slashes (shouldn't have any)
- Ensure protocol is
https(nothttpin production) - Update the OAuth app configuration in the provider
Collate SSO Credentials Not Auto-Populating
Problem: Collate SSO option doesn't show OAuth credentials
Solution:
- Verify Google OIDC SSO is configured correctly (Settings → Security → SSO)
- Collate SSO currently only supports Google OIDC
- Check that the SSO provider is Google:
- Google OIDC → BigQuery
- Ensure Google SSO OAuth app has required scopes (e.g., BigQuery API scope)
Users Cannot Connect After Configuration
Problem: Configuration saved successfully but users see "Service not available"
Solution:
- Verify Enabled is checked
- Check that users are accessing the correct service in SQL Studio
- Review backend logs for configuration errors
- Test the connection using test credentials
Next Steps
After configuring SQL Studio:
- Inform Users: Let users know SQL Studio is available for the configured services
- Share Authentication Guide: Direct users to User Authentication
- Monitor Usage: Review query logs and audit trails in Settings → Audit Logs
- Optimize Settings: Adjust Max Result Size and user-configurable fields based on usage patterns
Ready for users to connect? Guide them through User Authentication to establish their first connection.